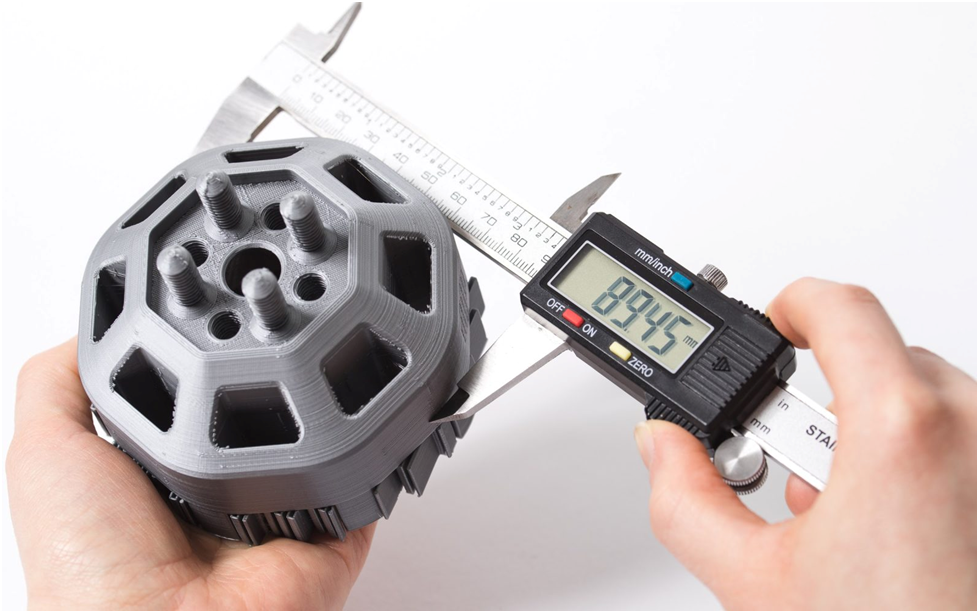

What is the accuracy of 3D printing? It’s a valid question to ask before incorporating the technology into your business operations. The type of 3D printing technique utilised, the quality of the 3D printer model, the 3D printing materials used, the intricacy and viability of the design, and the user-defined printing factors are all elements to consider factoring in improving the accuracy of the technology.
Read on to get a general overview of 3D printed parts and their dimensional accuracy. The article will also analyse how different technologies differ in accuracy and how users can improve the accuracy of their parts. But first, let’s get an in-depth knowledge of dimensional accuracy in online 3D printing, theprecision of various 3D printing technologies, and the factors that affect the accuracy of 3D printed parts.
Decoding Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy in 3D printing is a simple concept. It describes how well a printed part or prototype meets the original design’s desired dimensions, such as size and specifications.It is the measure of how close a printed part is to the digital version, and is commonly stated as a percentage or in millimetres, such as 1% or 0.5 mm. The phrases “accuracy” and “tolerance” are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to the degree of variance from the part’s actual and intended dimensions.Customers specify an acceptable tolerance range based on the importance of the dimensions and features upon which wholesale printing design service manufacturermay commence operation.
Gauging the Accuracy of the Most Popular 3d Printing Technologies
SLS-
Selective laser sintering, or SLS, is a 3D printing technique that uses a laser to combine powder particles, usually nylon. SLS printers are accurate, but their major draw is their capacity to make complex geometries since they don’t require any support structures to print. An SLS 3D printer’s accuracy is roughly 0.3 mm.
FDM-
Fused deposition modelling, or FDM, is a popular 3D printing technology that produces rapid prototypes and functional components. Industrial FDM 3D printing has a 0.15 percent dimensional tolerance and a lower limit of 0.2 mm.
Resin–
SLA and DLP photopolymerization printing technologies use a light source such as a projector or a laser to cure photosensitive resins. These precise technologies are utilised both professionally and otherwise, and some machines are not that expensive as FDM. A desktop resin 3D printer’s accuracy is roughly 0.1 mm. A professional resin 3D printer’s accuracy is roughly 0.01 mm.
Metal 3D Printing–
The most prevalent 3D metal printing services use methods comparable to selective laser sintering. Metal particles are heated and layered together. Warping is a recurring problem because these layers may cool at different temperatures. Metal 3D printing calls for support structures. A thermal stress release procedure is also frequently used to prevent warping after production. It has a dimensional tolerance of 0.1 mm.
Material Jetting–
Material jetting is the least common 3D printing technology, but it is highly accurate since it does not use heat, which causes distortion such as warping. The accuracy rate is roughly 0.05 mm.
Factors Impacting Dimensional Accuracy
Quality of the printer-
The difference between low-cost and high-end 3D printing machines is enormous. For instance, SLA 3D printers are generally more accurate than FDM printers, but an elementary SLA printing machine will generate less accurate parts than a feature rich FDM printer.
Material-
It is easier for some materials to be printed than others, making them more suited to accurate part fabrication. Non-standard materials such as high-temp filaments, flexible filaments, and alloys containing precious metals often sacrifice printability to save their unique attributes.
Component design-
Even the most advanced 3D printers will find it hard to accurately 3D print a poorly designed part. Printing long and thin features, especially those without proper support, can be challenging, and printing large parts can also be problematic. In general, designs should not include details that are too small for the printer to handle.
Warping and shrinking-
The most common deformations during 3D printing are warping and shrinkage. Because the deformations impact the final shape and dimensions of the part, the ones that show evidence of warping and shrinkage will be less accurate than those that do not. In most cases, the deformity is minor. However, it is crucial to strive to limit these undesirable impacts to critical parts.
Parameters for printing-
Users can experiment with their 3D printer settings to achieve various outputs, in addition to calibration, which is required for quality prints. Some parameter setups print more quickly, while others print more accurately.
Post processing decisions-
The accuracy of the final product can be affected or preserved by decisions made during the last phases of production. Proper cooling should be followed to retain items in the desired shape.
Quick Tips to Improve Dimensional Accuracy
Try these tips to improve the dimensional accuracy once you’ve picked the right 3D printing technology: –
- Don’t forget to calibrate your 3D printer regularly or before any big assignment.
- Keep the printer in mind while designing the parts. Simplify or remove any complex design features.
- When printing parts, use support structures to keep them stable. Remove supports with caution to avoid damaging or altering their final dimensions.
- Choose standard materials that are less prone to warping unless a specific detail is desired.
- To retain a consistent temperature across the component and decrease distortion, use a heated chamber (SLS/Metal) or a heated print bed (FDM).
- Reduce printing speeds by lowering the flow rate and other settings. Slow printing can help reduce inaccuracies, but too great of a reduction can create other issues.
Final Thoughts
Because prototypes will be reviewed and verified later, dimensional accuracy is essential. As a result, it’s critical to minimise the margin of error. If you reside in Australia and are seeking 3D printing services, Google “3D printing stores near me” to uncover a variety of options in 3D printing Sydney,3D Printing Adelaide, and other cities. A professional organisation that provides 3D printing service Sydney and 3D printing service Adelaide offers a variety of services that are extremely effective and tested to ensure the maximum dimensional accuracy of your 3D printed part.












